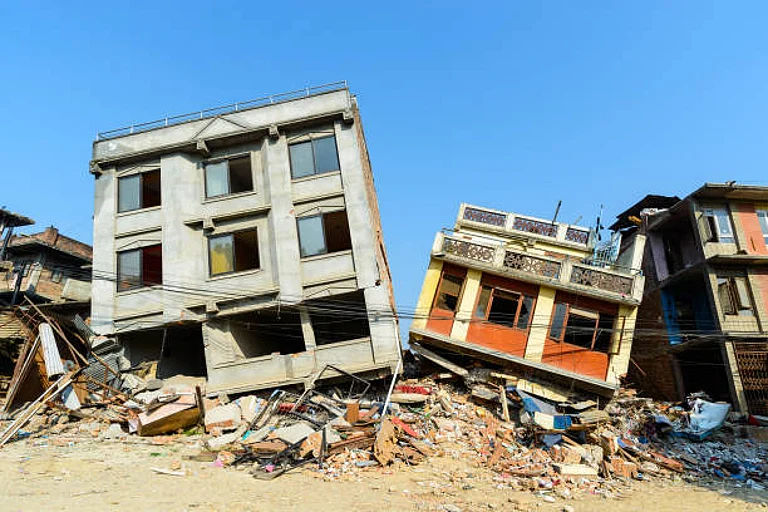
A strong 7.7 magnitude earthquake rocked central Myanmar on March 28, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS). The tremors caused a skyscraper under construction in Bangkok to collapse and toppled buildings in neighbouring Myanmar, where Myanmar’s ruling junta declared a state of emergency in some areas, according to Reuters.
At least three people were killed in the town of Taungoo in Myanmar when a mosque partially collapsed, reported Reuters, while at least two people reportedly died and 20 were injured after a hotel collapsed in Aung Ban.
In Thailand, at least one person was killed and dozens of workers were rescued from under the rubble of the skyscraper that had been under construction in Bangkok, Reuters revealed.
Bangkok's city authorities declared the capital a disaster-stricken area, saying they needed to assess and monitor damaged areas and assist people who might still be at risk.
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) said that the earthquake, which struck in the afternoon, was of 7.7 magnitude and at a depth of 10 km (6.2 miles). It was followed by a powerful aftershock.
The epicentre was about 17.2 km from the Myanmar city of Mandalay, which has a population of about 1.5 million.
Myanmar's ruling military declared a state of emergency in multiple regions.
"The state will make inquiries on the situation quickly and conduct rescue operations along with providing humanitarian aid," reported Reuters.
Vulnerability to Earthquakes
The recent earthquake underscores Myanmar’s vulnerability to earthquakes, which is primarily due to its location along the Sagaing Fault, a major tectonic boundary between the Indian Plate and the Burma microplate, according to India Today.
According to a ScienceDirect study, the Sagaing fault runs over 1,200 kilometres through the country and has a history of significant seismic activity.
The region’s vulnerability arises from the ongoing collision of tectonic plates, which increases the likelihood of earthquakes.